The 27th annual Computational Cell Biology workshop (online) will take place March 16-20, 2026. Register here.
New VCell version 7.7.0 (build 47) is realeased on February 4, 2026. If your VCell is not updated automatically, please go to https://vcell.org/run-vcell-software, download and install a new version.
New VCell 7.7 is released: any kinetic laws can be simulated stochastically; simulation results can be sent to ImageJ for analysis; Single Sign On browser-based login.
Check lectures and tutorials from the 26th ONLINE Annual Workshop on Computational Cell Biology at our YouTube channel https://www.youtube.com/@compcellbiol8898.
VCell
VCell (Virtual Cell) is a comprehensive platform for modeling cell biological systems that is built on a central database and disseminated as a web application.
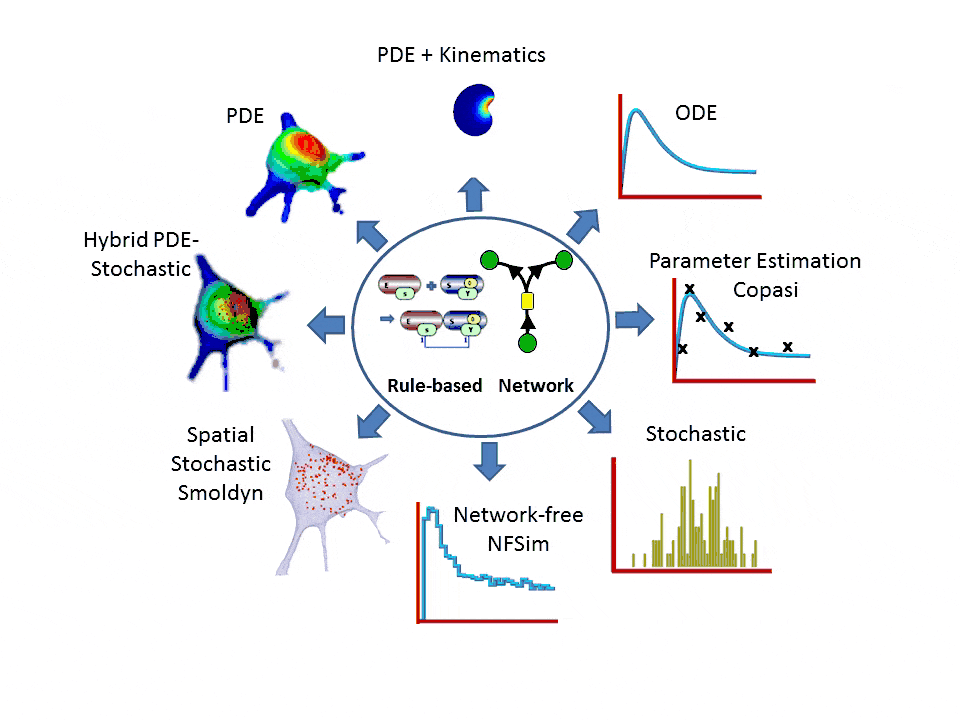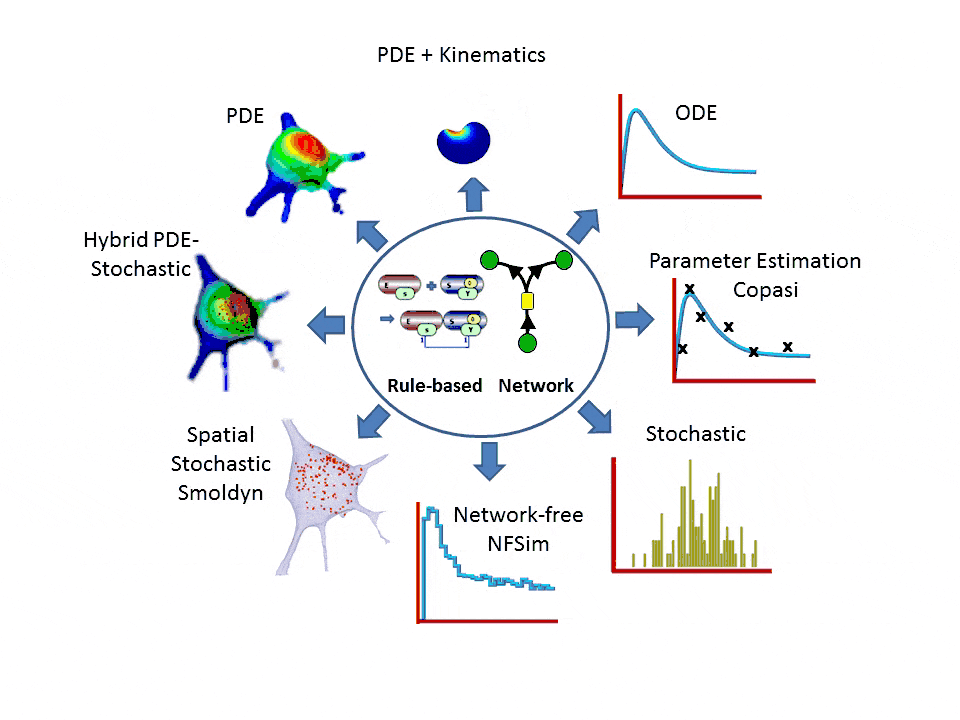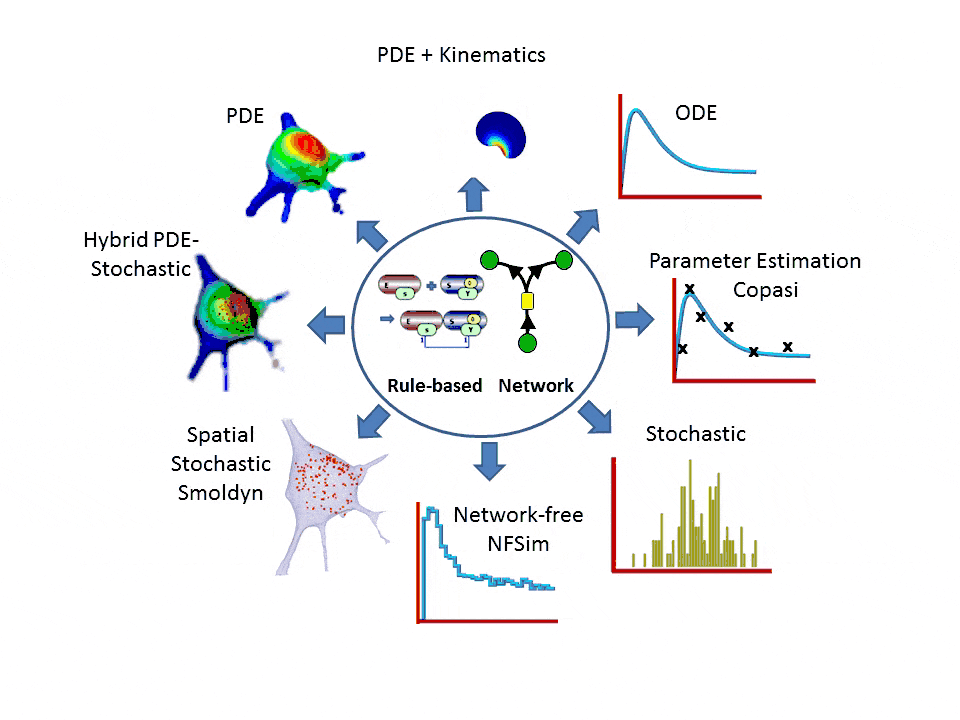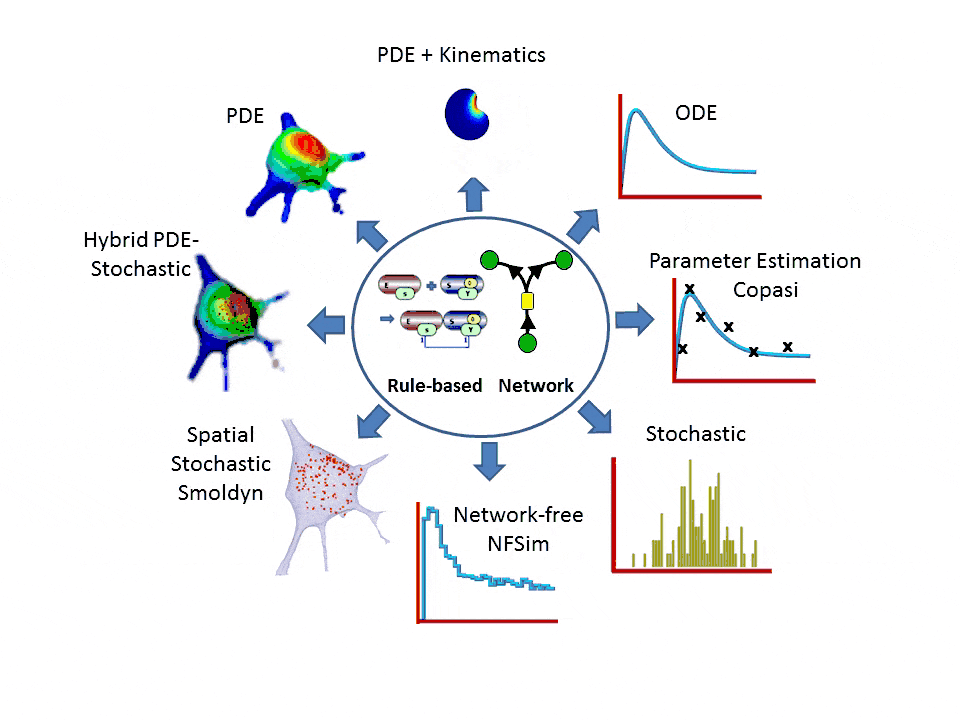
- One-stop simulation shopping: deterministic (compartmental ODE or reaction-diffusion-advection PDE with support for 2D kinematics), stochastic reactions (SSA solvers), spatial stochastic (reaction-diffusion with Smoldyn), hybrid deterministic/stochastic and network-free agent based simulations. Support for membrane flux, lateral membrane diffusion and electrophysiology.
- Explicit network or graphically expressed rules can be used to model
- Free with automatic installers for Windows, Mac OS and Linux.
- Biology-based interface for inexperienced modelers; enter reactions and pathways and VCell automatically creates the math for you. Experienced modelers can enter math directly.
- Our remote servers can run complex simulations from any low-cost laptop
- Geometries from 2D or 3D microscope images or from idealized analytical expressions.
- Access models and simulations from anywhere using the VCell database; models can be shared among collaborators or made publicly available.
SpringSaLaD
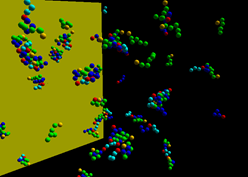 SpringSaLaD is a stand-alone software tool to explicitly model binding events and state changes among multivalent molecules. It is one of the first algorithms to account for crowding effects within multimolecular clusters. Spring SaLaD models proteins as sets of reactive sites (spheres) connected by stiff springs. The impenetrable spheres capture excluded volume and steric hindrance effects. Langevin dynamics are used to model diffusion of each reaction site, and binding reactions are governed by probability based on diffusion coefficients of the sites, the site radii and the macroscopic on rate. Go here to download the software or read more about the about Spring SaLaD.
SpringSaLaD is a stand-alone software tool to explicitly model binding events and state changes among multivalent molecules. It is one of the first algorithms to account for crowding effects within multimolecular clusters. Spring SaLaD models proteins as sets of reactive sites (spheres) connected by stiff springs. The impenetrable spheres capture excluded volume and steric hindrance effects. Langevin dynamics are used to model diffusion of each reaction site, and binding reactions are governed by probability based on diffusion coefficients of the sites, the site radii and the macroscopic on rate. Go here to download the software or read more about the about Spring SaLaD.
Computational Cell Biology
CompCellBio.org (opens in a new tab) is designed to provide a central site for access to software, model repositories, quantitative repositories and educational resources for computational cell biology research. Developed under the NIGMS National and Regional Resources funding that maintains COPASI (opens in a new tab) and Virtual Cell (VCell), two of the most powerful modeling environments for computational cell biology, the website provides the broader community with information and resources to aid in the development of computational models of cell biology.
Who Are We?
The Virtual Cell was developed with funding from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) (opens in a new tab) as a Biomedical Technology Research Resource at the Center for Cell Analysis and Modeling (CCAM), and is currently funded by R24 GM137787. CCAM continues to develop new technologies for mathematical models of cell and systems biology through development of new physical formulations of biological mechanisms, developing the numerical methods for mathematically simulating these mechanisms, and bulding software infrastructure to deliver these tools for different types of modeling applications including large reaction network applications, spatial applications and detailed molecular interactions. Meet the VCell Team.
Where Are We?
VCell is developed at The Center for Cell Analysis & Modeling (opens in a new tab), at UConn Health (opens in a new tab). Established in 1994, CCAM consists of faculty trained in diverse backgrounds from chemistry, physics, and experimental cell biology to software engineering. Research at CCAM focuses on the development of new approaches for in vivo measurements and manipulation of molecular events within the cell, as well as new computational approaches to organize such data into quantitative models. CCAM is home to the Microscopy Facility (opens in a new tab), housing numerous extensive fluorescent imaging microscopes, and the High Performance Computing (opens in a new tab)facility.
Please acknowledge the VCell Resource in all publications. VCell is supported by NIH Grant Number R24 GM137787 from the National Institute for General Medical Sciences. And please reference the appropriate citations.
Employment
Please see the CCAM Employment page for opportunities.
News
For additional posts see News & Events.
New VCell does not need admin privileges to install
2026-02-03. The new VCell release (7.7.0 build 47) does not need admin priviledges to install. To switch to a new version, a user still need admin priviledges to uninstall the previous version, but from now on, local users will be […]
Modeling of EGFR-ERK-Raf signaling
2026-02-03. Researchers at UConn, UPitt and U Virginia used VCell to model systems-level consequences of low RAF abundance for EGFR-ERK signaling
Biophysical Journal. 2026 Feb 3;125(3):881-900.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/41496453/
VCell at CellBio 2025
2025-12-10. VCell was represented at the American Society of Cell Biology Annual Meeting 2025 in Philaderplphia. On Sunday, December 7th, Michael Blinov together with James Faeder (UPitt) and Margaret Johnson (JHU) presented rule-base modeling methods for Biophysical Modeling of the […]
3D reaction-diffusion model of Tau-microtubule dynamics
2025-11-19. Researchers at several Japanase Universities used VCell to model graded regulation of microtubule-binding of Tau by the phosphorylation state of the proline-rich region in living neurons:
Nakata, R., Torii, T., Miyasaka, T. and Misonou, H., 2025. Graded regulation of microtubule-binding […]
Modeling FRAP to study germination of spores of Bacillus species
2025-10-23. Researchers at UConn and University of Cambridge (UK) used VCell to model FRAP in their studies of resistance and germination of spores of Bacillus species lacking members of a spore integral inner membrane protein family and locations of these […]
VCell Partners
-VCell acknowledges our collaborative partners that enhance VCell capabilities
-Software Associates
VCell uses Install4J, a multi-platform installer builder to create our executables.














